LCC
Nanoparticles for health
The case of contrast agents in medical imaging.
Our research activities focus on the design, synthesis and evaluation of hybrid nanoparticles as single or dual mode imaging platforms, potentially targeted.
Our objective is to improve the benefit/risk ratio and patient comfort when the use of a contrast agent is necessary for a reliable diagnosis in medical imaging. This implies in particular the design of more efficient contrast agents in order to reduce the doses to be injected. This can be achieved by immobilising molecular contrast agents on chemically inert nanoparticles (e.g. silica) or by developing nanoparticles with remarkable properties adapted to the targeted imaging technique (e.g. high magnetisation for use in MRI). Their coating with a layer of silica is preferred to facilitate their surface functionalisation (biocompatibility, vectorisation, stealth, etc.).
The combination of these two approaches leads to bimodal probes which makes it possible to use two imaging techniques, chosen as complementary (MRI/CT, MRI/fluorescence, T1/T2 MRI…), in a very short time (ideally synchronously) and with a single injection.
These projects are carried out in collaboration with:
- in Toulouse : laboratories SPCMIB, ToNIC, CEMES et CERTOP
- in Belgium : University of Mons
- in Spain : Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
- in the US : Florida State University
Examples
- Faraday Discuss., 2014, 175, 97-111, doi.org/10.1039/C4FD00105B
- Molecules, special issue on Nanomaterials for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy, 2019, 24(24), 4629, doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244629 ; New J. Chem., 2020, 44, 18031 – 18047, doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ04430J ; Bioconjugate Chem., 2022, 33(5), 881–891, doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00116 ; Molecules, 2024, 29 (7), 1537/1-65, doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071537
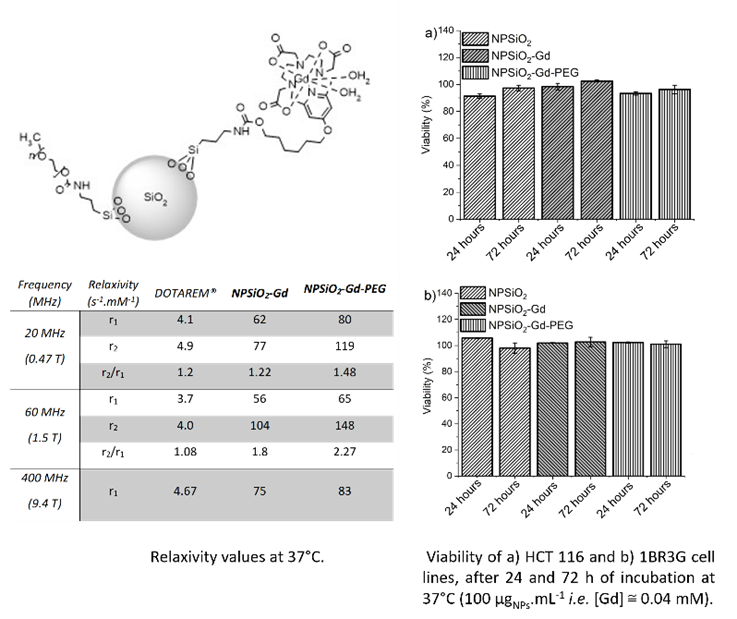
New J. Chem., 2020, 44, 18031 – 18047, doi.org/10.1039/D0NJ04430J
LCC CNRS
Laboratoire de chimie de coordination du CNRS
205 route de Narbonne, BP 44099
31077 Toulouse cedex 4
France




