LCC
Nanoparticles and CO2 Valorization
The valorization of CO₂ as a C1 synthon is one of the strategies explored to help reduce this greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. Nanostructured materials can catalyze the transformation of CO₂ into platform molecules for fine chemistry or hydrogen storage (formic acid), as well as synthetic fuels.
Our research activity focuses on the development of nanocatalysts based on metals that are more abundant than the noble metals traditionally used in this field, in the form of monometallic or bimetallic systems, either composite or supported.
Example:
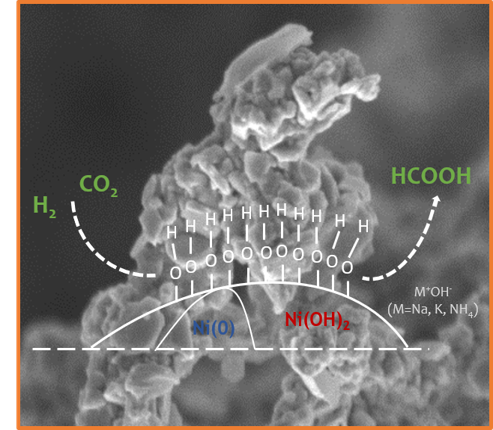
– An air-stable, reusable Ni@Ni(OH)2 nanocatalyst for CO2/bicarbonate hydrogenation to formate, X.-P. Fu, L. Peres, Jérôme Esvan, C. Amiens, K. Philippot, N. Yan, Nanoscale, 2021, 13, 8931-8939 (doi.org/10.1039/d1nr01054a).
Collaboration with Professor Ning Yan’s team at the National University of Singapore (NUS).
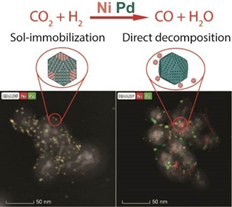
– Structure and activity of supported bimetallic NiPd nanoparticles: influence of preparation method on CO2 reduction, A.H. Braga, N.JS. Costa, K. Philippot, R. V. Gonçalves, J. Szanyi, L. M. Rossi, Chem.Cat.Chem., 2020, 12, 1-11 (doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201902329).
Collaboration with the group of Pr Liane Rossi at the University of Sao Paulo, Brasil.
LCC CNRS
Laboratoire de chimie de coordination du CNRS
205 route de Narbonne, BP 44099
31077 Toulouse cedex 4
France




